The results of the research show that Arvan Cloud is the best cloud service provider in the TTFB index of Iranian sites with a share of 86%, and Cloudflare ranks second in this index.
According to Iran digital economy annotation, this indicator measures the duration of the first HTTP request from the user to the site server and its return ( Time To First Byte ). The importance of TTFB is that it is one of the most effective indicators of the page loading speed of any website, and studies show that using a CDN is effective for improving this index.
Arvan Cloud’s latest TTFB index survey of nearly 5,692 domains that were in GoogleCrux data and using CDNs showed that 86% of domains in Good status are using Arvan’s CDN.
– 29% of domains that used Arvan Cloud are in good condition.
– 4% of domains that used Cloudflare are in good condition.
– The average condition of five other provinces in this index is 5% in good condition.
It should be noted that the domains classified as Poor or Need Improvement in this index may be in this situation due to a mistake in the configuration, and it is not necessarily related to the CDN function of that domain.
The importance of TTFB in measuring the speed of domains
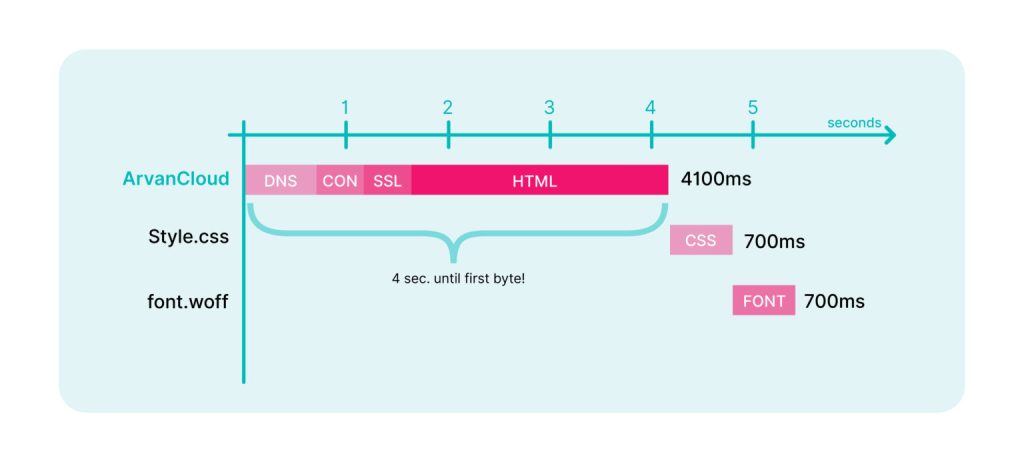
In the simplest definition, the time interval from the moment the user’s browser sends an HTTP request to a web server until the first byte of the response is received from the server is called TTFB. This indicator includes the time taken to establish a connection, send an HTTP request, and start receiving a response. In fact, this measure shows the responsiveness and speed of a web server or network.
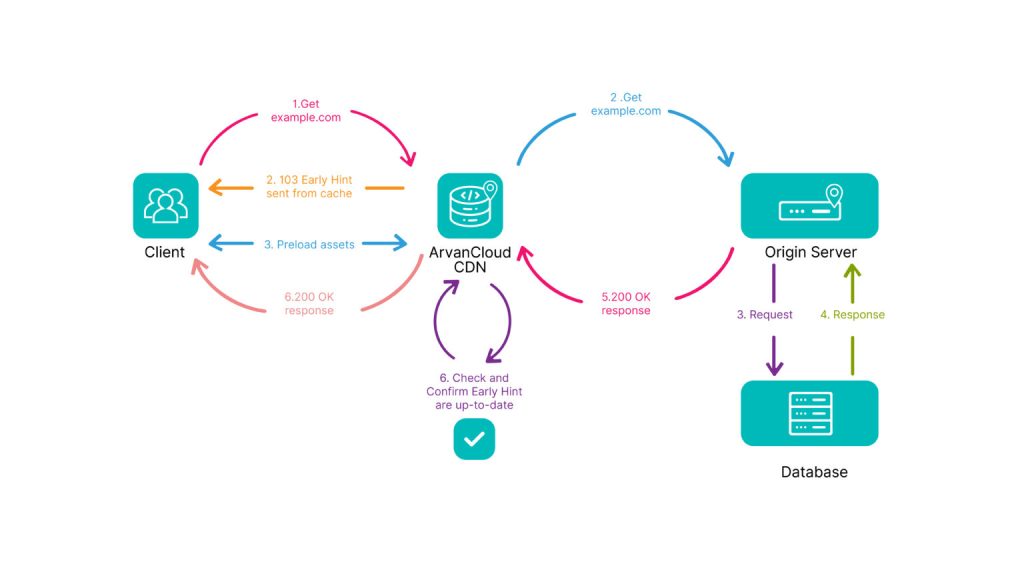
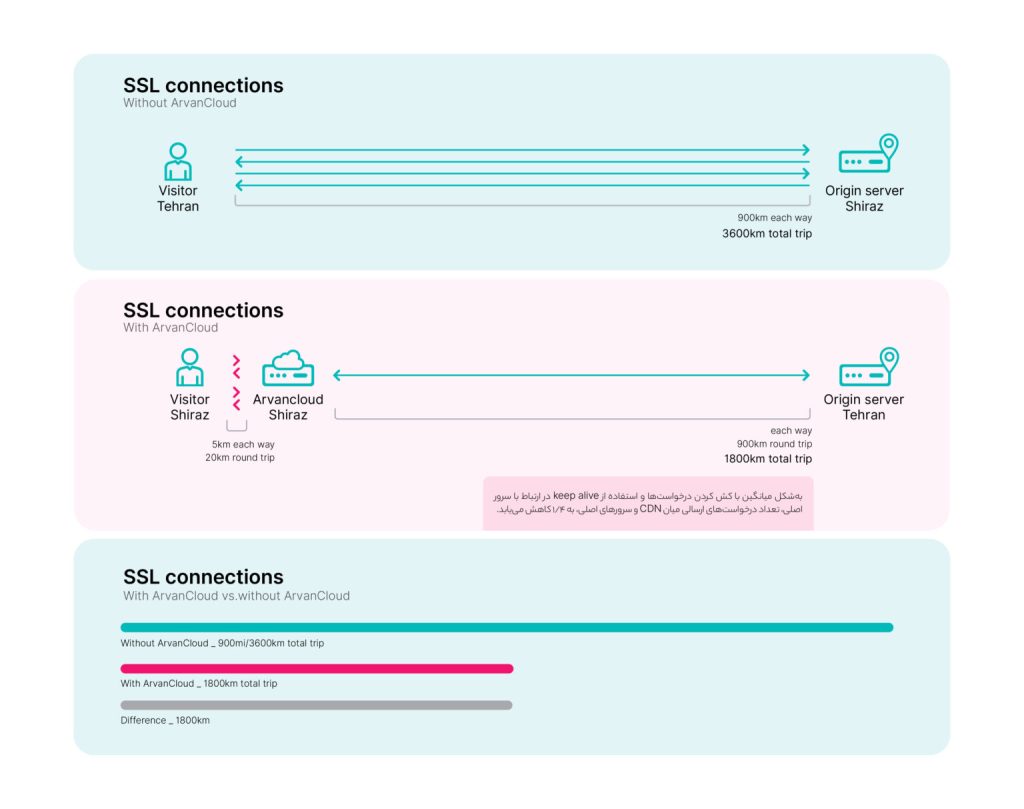
Exactly like the path shown in the diagram below:
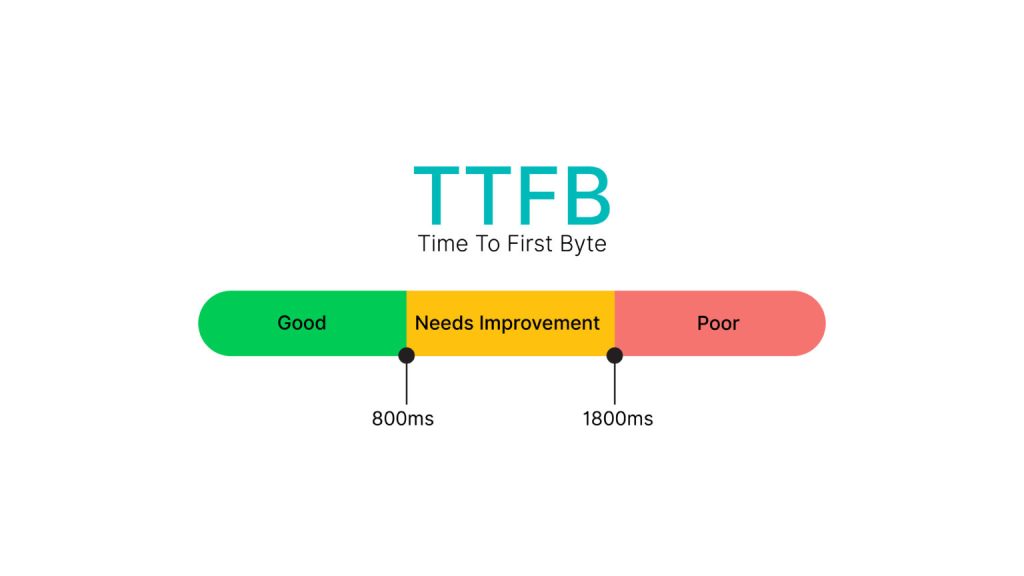
The importance of this index is very important for analyzing the performance of websites; A lower TTFB means that the website content loads faster, and a lower TTFB means that the user experience and SEO of the site are in good shape. Factors such as network latency, server load, and website optimization can affect TTFB. The size of TTFB means the amount of delay time in loading the content and the amount of measurement of this index is divided into three parts; Good is less than 800 milliseconds delay in sending data, poor is more than 1800 milliseconds and Needs improvement is between these two spectrums.
Of course, it should be kept in mind that the domains that do not receive a good number in this index may be due to a mistake in the configuration and are not related to the CDN function of that domain.
Why is TTFB more accurate than Round-Trip Time RTT?
Although there are criticisms of this index (Time To First Byte), it is still the most important criterion for measuring the speed of websites. In some studies, it has been determined that there are better indicators that provide a more accurate representation of the performance of a server or content delivery network for end users. The dominant metric used to measure request round-trip time (RTT) is the amount of time it takes for a request to be sent from an end user to a cloud provider and back. For example, Cloudflare’s average RTT is 50 milliseconds for 95% of the population connected to Cloudflare.
But the important issue about this index is that it does not necessarily show the quality of users’ requests. This is where TTFB comes into play; which measures the time between sending a request from the end user and the first response.
The closest distance to Iranian users to international pop site providers
In addition to the points mentioned above, in this report we tried to more accurately calculate the amount of time a request from Iran is sent to a CDN popsite and returns (that is, CDN performance for each cloud provider); Our findings in Arvan Cloud and Cloudflare reports show that the state of CDN Performance of cloud providers is different.
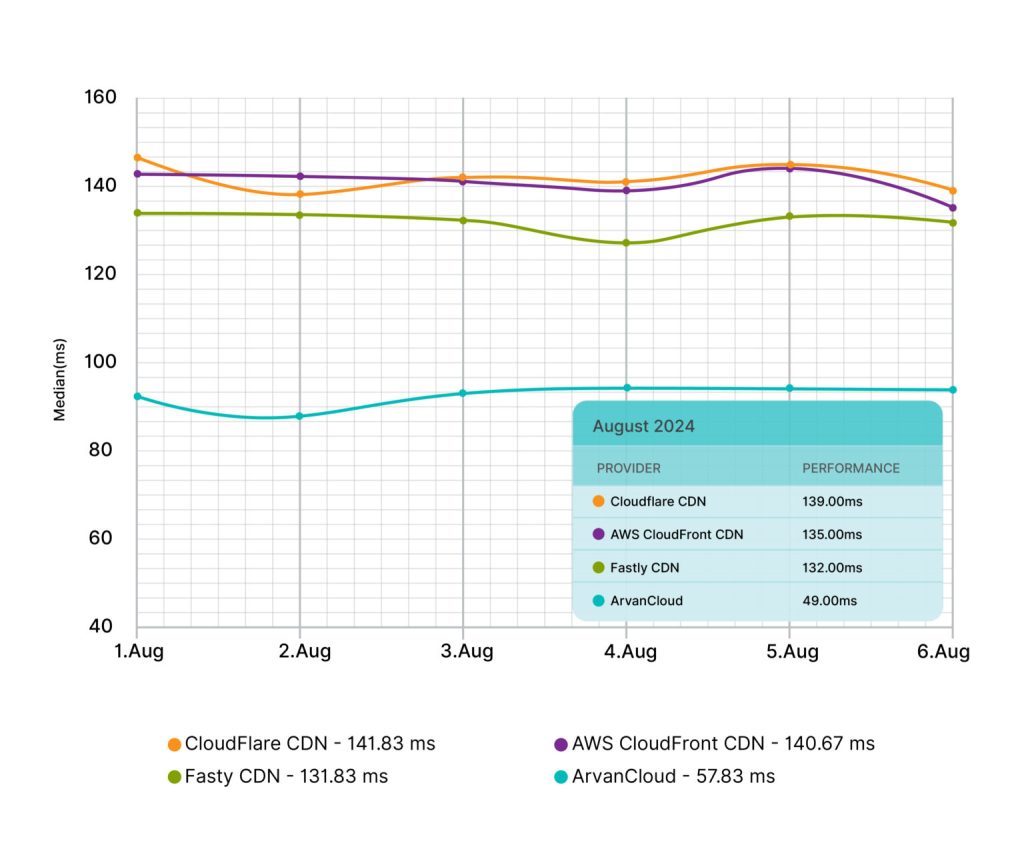
The closest distance between an Iranian user and an international pop site provider is related to Arvan Cloud with 49 milliseconds.
According to the same survey, after Arvan Cloud, Fastly with 132 milliseconds, AWS with 135 milliseconds, and Cloudflare with 139 milliseconds are the closest international pop site providers to Iranian users.
What does the TTFB index say about the speed of Iran’s cloud market?
Iran’s cloud market speed; Most domains “need improvement”!
Review method: To select Iranian domains, we used Google Crux as a selection criterion. This database is an important reference for evaluating the TTFB index of domains due to the widespread use of Internet users in all countries. After the placement criterion of this database, we selected the domains that use CDN in Iran and evaluated them separately by cloud provider.
Then we extracted the TTFB size of each of these sites from Google Crux data. As previously , according to Arvan Cloud’s latest market research , Arvan Cloud’s share of CDNs in the country was nearly 60%. In this report, Arvan Cloud’s CDN speed quality in Iranian domains has a similar ratio.
In more detail, it can be said that among the 5,600 domains examined, nearly 2,500 domains use Arvan, of which 736 domains are in good condition, and 77 domains are in good condition out of 2,119 domains that use Cloudflare. Out of a total of 468 domains from cloud provider number three, 12 domains in good condition, out of a total of 236 domains from cloud provider number four, 8 domains in good condition, out of 180 domains from cloud provider number five, 15 domains in good condition, out of 96 domains from cloud provider number Six, 4 domains are in good condition and 4 out of 36 domains of cloudprovider number seven are in good condition.
Why CDN is one way to improve TTFB situation?
CDNs can be effective in improving the situation of TTFBs because they solve the problem of proximity of the user to the main server by using a distributed network of servers. CDNs store resources on servers that are physically closer to users and may also provide benefits beyond edge servers; In a simpler explanation, it should be said that CDNs reduce the path of sending requests from the user to the server.
As it is clear from the diagram above, it shows the impact of the speed and data transfer from the user to the nearest cloud provider. In fact, in any simple internet connection, before the user’s main request is sent, there are back and forth between the user and the server, which if a CDN is placed in this path, it will reduce the amount of back and forth from the user to the server to the user’s path to the nearest CDN.
In the end; How to measure site TTFB?
Web Vitals is a website speed measurement solution, the test version of which was recently made available to the public by Arvan Cloud.
isna.ir: This site works based on the Google Crux database. In fact, according to the data saved by Google Chrome, Google stores all the data related to the user’s UX (one of which is TTFB). This trial version is also defined based on the Google Crux database, and in fact, by entering the desired origin address, users can check the information related to its speed in the Google database and in their 6 main indicators. displays Also, in the following, solutions are suggested to improve the possible situation of these indicators.
Briefly about the domain speedometer family (Web Vitals):
FCP:First Contentful Paint
This indicator, with a 10% improvement effect, refers to the time when the user can see the first image of the site with its full content. In other words, when the website is fully loaded and its content is downloaded, the time taken is called FCP or First Contentful Paint; CDN (or content distribution network) can improve the website’s position in this index by optimizing and compressing the image.
LCP (Largest Contentful Paint)
This measure has a 25% impact on improving the speed of domains and is one of the most important factors affecting the site’s performance score. In fact, this indicator shows how long it takes for the user to see the largest content of the site on the screen and is known as LCP, which stands for Largest Contentful Paint. The above three criteria were related to the performance of the site, which has a total of 45% impact on the domain speed performance score.
TTFB (Time to First Byte)
The time to receive the first byte or Time to First Byte (TTFB) is the time when the first byte of the response is received after sending the request. While measuring this time interval, the system also calculates the time required for DNS lookups and network delays.
CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift)
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) is one of the main metrics in evaluating websites’ performance and user experience (UX), specifically defined in Google’s Core Web Vitals set. CLS is a metric for measuring the visual stability of a web page. CLS refers to the amount of unexpected changes that occur in the layout of a web page during loading and user interaction. In other words, CLS measures the amount of sudden “jumps” of page elements (such as text, images, buttons, etc.) that move without any user intervention.
INP (Interaction to Next Paint)
Interaction to Next Paint (INP) is a new metric introduced by Google and considered to replace FID in evaluating the performance of websites. While FID only focused on the user’s first interaction with the page, INP more comprehensively and accurately examines all user interactions with the page during a browsing session.
(FID) First Input Delay
One of the key metrics in evaluating the performance of websites is the user experience (UX) introduced by Google, which refers to the time between the user’s first interaction with the page (such as clicking a button or link) and when the browser actually Responds to this interaction, passes. In other words, FID is the amount of time the browser needs to respond to the user’s first interactive action.




No Comment! Be the first one.